
Normal radiographic anatomy of the elbow Radiology Case Radiopaedia
The lateral elbow view is part of the two view elbow series, examining the distal humerus, proximal radius and ulna. It is deceptively one of the more technically demanding projections in radiography 1-3. The projection is the orthogonal view of the AP elbow allowing for examination of the ulna-trochlear joint, coronoid process, and the.
Mnemonic Approach to Elbow Xray FOOL Epomedicine
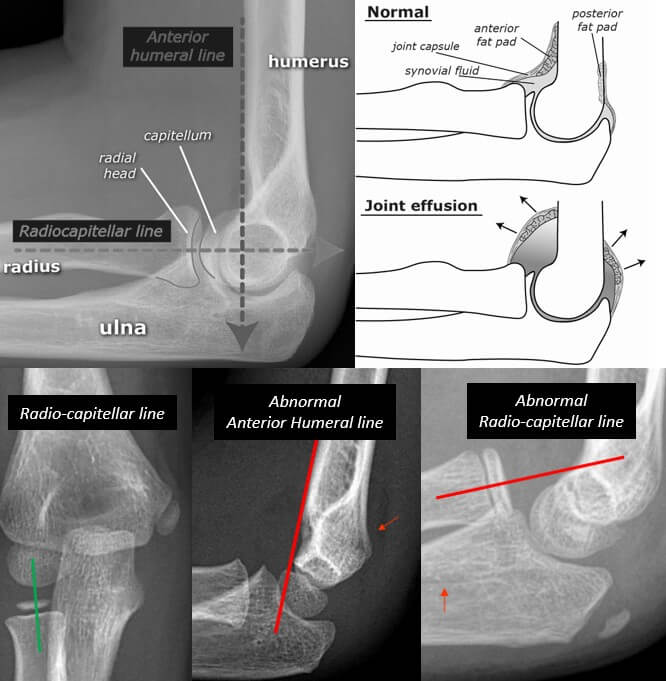
How to read an elbow x-ray. Fractures lines can be difficult to visualize after acute elbow injury, particularly in children. Below are eight sequential steps to aid in the radiographic recognition of occult signs of injury. Steps: Hourglass sign/figure of eighty Anterior fat pad evaluation Posterior fat pad evaluation Anterior Humeral line.
Musculoskeletal Undergraduate Diagnostic Imaging Fundamentals
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. The elbow series is a set of radiographs taken to investigate elbow joint pathology, often in the context of trauma. It usually comprises an AP and lateral projection, although other non-standard, modified projections are utilized for specific indications.
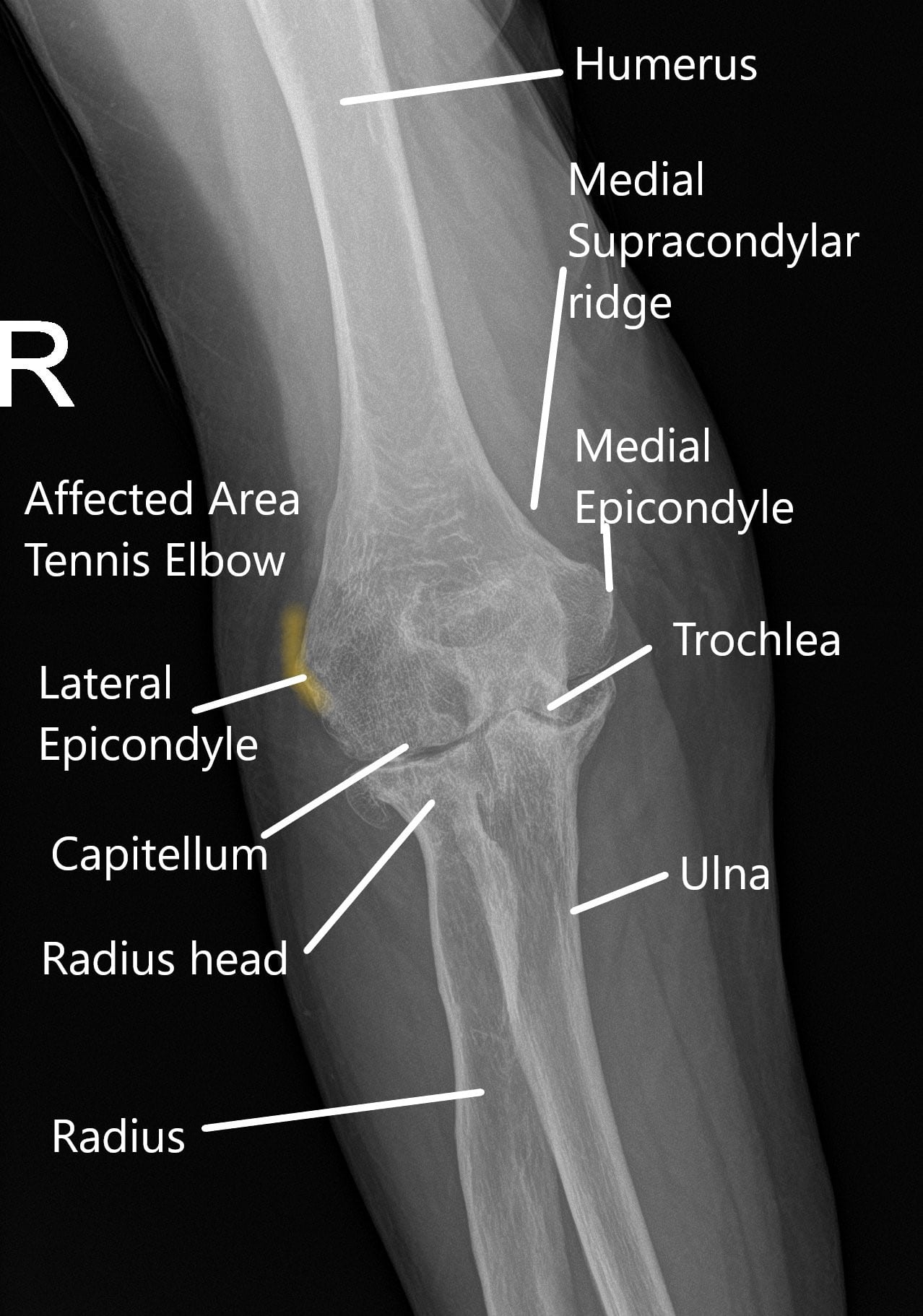
Tennis Elbow Joint Pain, Causes and Management Complete Orthopedics
Labeled Elbow XRay Anatomy - AP View #Anatomy #Radiology #Elbow #XRay #AP #Labeled

Anatomy of Elbow Xrays YouTube
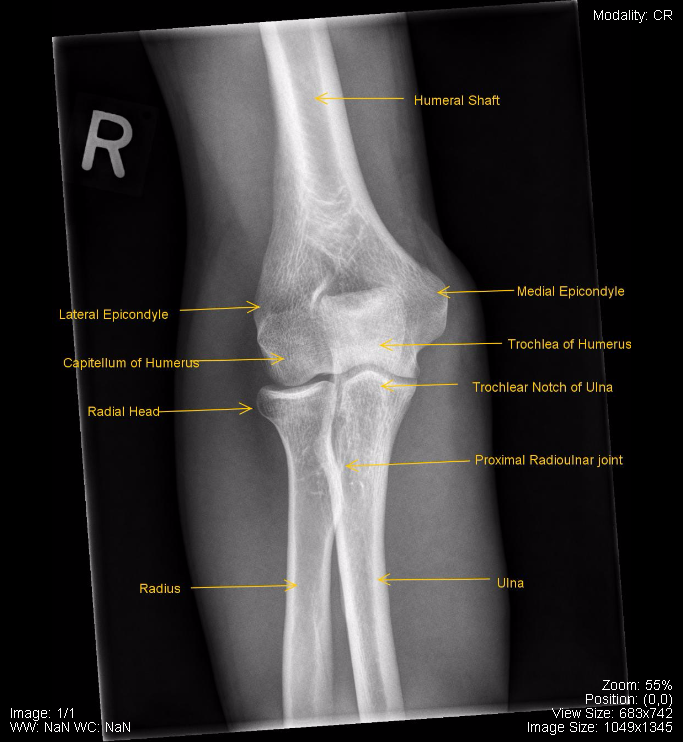
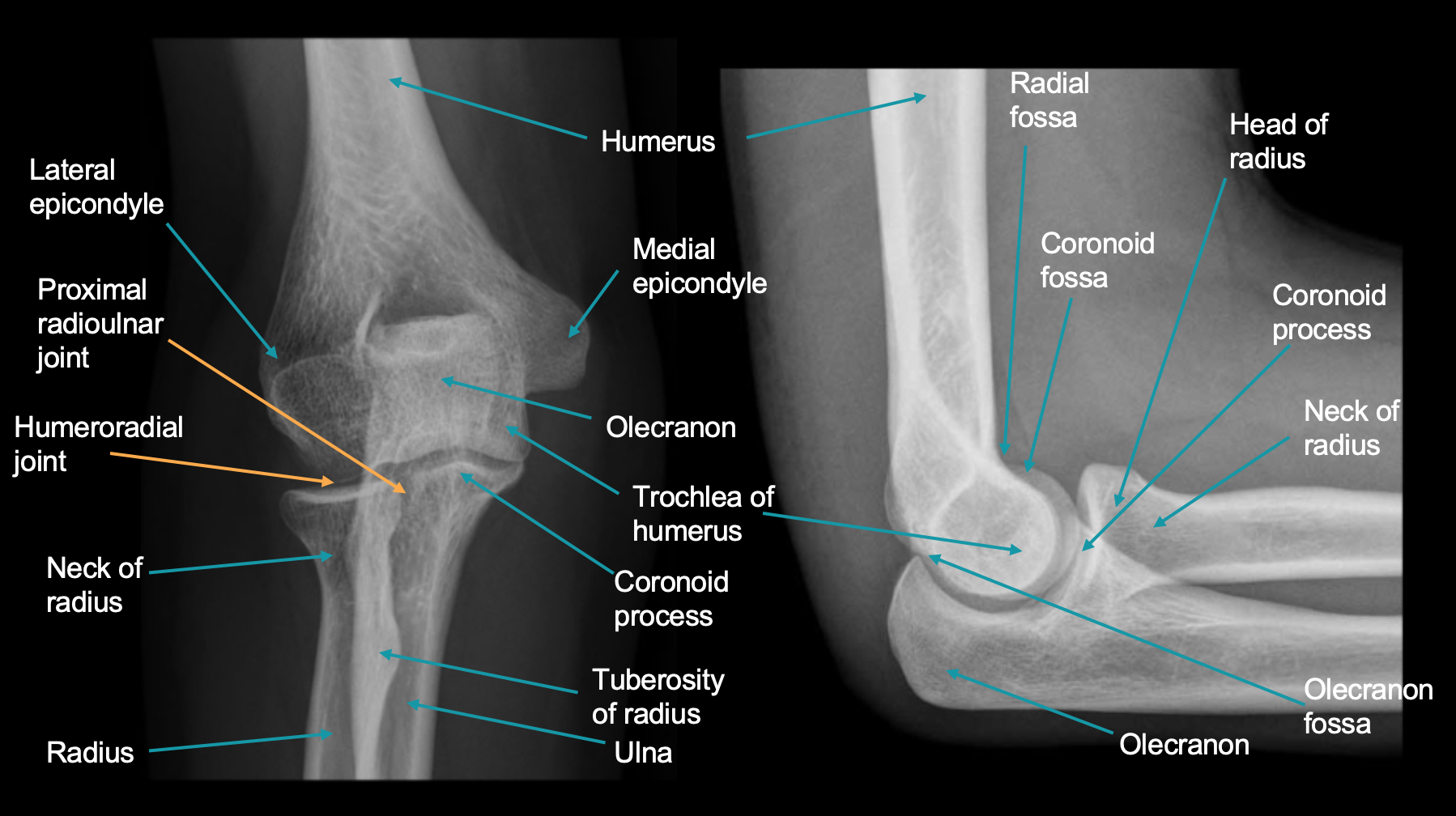
Review the ossification centers of the elbow, they should appear in the following order 3 : capitellum: 2-24 months. radial head: 3-6 years. internal (medial) epicondyle: 4-7 years. trochlea: 8-10 years. olecranon 8-10 years. external (lateral) epicondyle: 10-13 years. Understanding the order is important, and systematically reviewing the.
EPOS™
Radiology. Radiography is typically the first imaging study performed in the setting of elbow pain following acute trauma or in the setting of a suspected overuse injury. Standard radiographic examination of the elbow should include an anteroposterior view and a "true" lateral view, and occasionally oblique views may be of benefit.

Imaging of Elbow Fractures and Dislocations in Adults in 2023
Check the anterior humeral line: drawn down the anterior surface of the humerus. should intersect the middle 1/3 of the capitellum. if it does not, think: distal humeral fracture. Check the radiocapitellar line: drawn along the radial neck. should always intersect the capitellum. if it does not, think: radial head dislocation or subluxation.

Lateromedial projection /Lateral Position ELBOW Radiology, Radiology
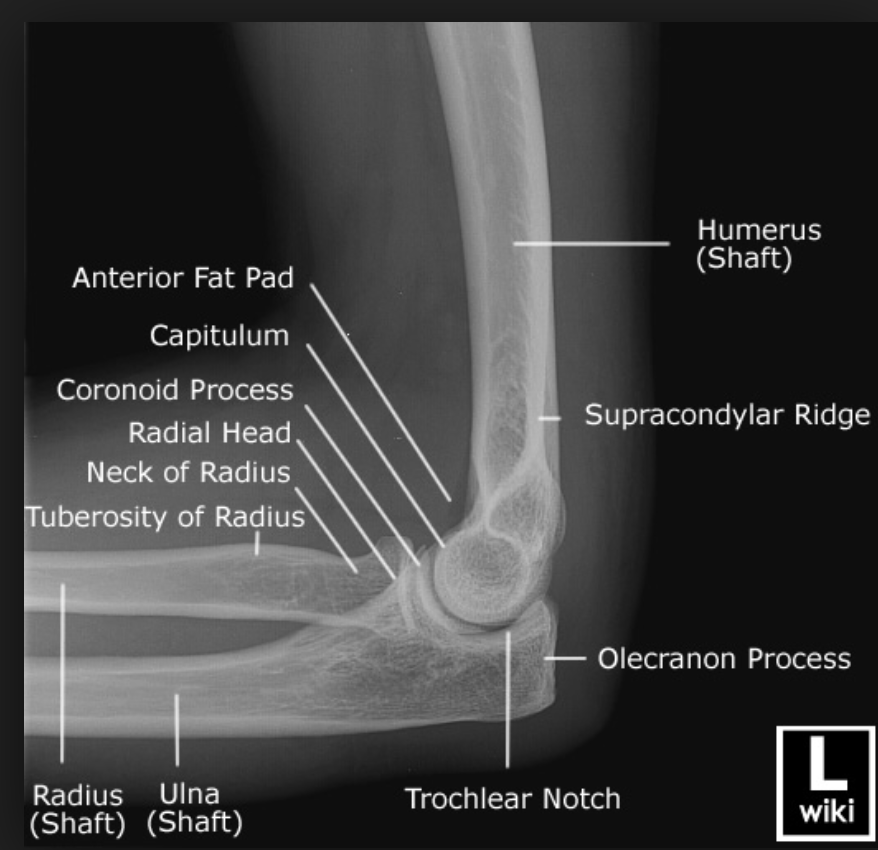
Humero-radial joint. Radial head. Radial neck. Radius (Shaft) Ulna (Shaft) Radial tuberosity. Proximal radio-ulnar joint. Humero-ulnar joint. Trochlea of humerus.
Elbow Dislocation Core EM
An elbow X-ray is a medical test that produces an image of the inside of your elbow. The image displays the inner structure ( anatomy) of your elbow in black and white. An elbow X-ray shows your soft tissues and elbow bones. Your elbow bones include the upper bone of your elbow joint (humerus) and the lower bones of your elbow joint (radius and.

Startradiology
The Anatomy of the Elbow. The elbow is a hinged joint made up of three bones, the humerus, ulna, and radius. The ends of the bones are covered with cartilage. Cartilage has a rubbery consistency that allows the joints to slide easily against one another and absorb shock. The bones are held together with ligaments that form the joint capsule.

Interpreting Elbow and Forearm Radiographs — Taming the SRU
MRI examination of the Elbow. by Mark Anderson. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center. This review is dased on a presentation given by Mark Anderson and adapted for the Radiology Assistant by Robin Smithuis. We will discuss: Basic MR techniques and MR.

elbow anatomy xray
anatomy at elbow. runs medial to brachial artery, pierces medial intermuscular septum (at the level of the arcade of Struthers) and enters posterior compartment. it traverses posterior to the medial epicondyle through the cubital tunnel. innervation at elbow. it gives branches to elbow joint.

The Elbow
This view is clinically indicated for trauma, chronic discomfort or infection of the elbow joint. It aids in visualizing fractures and/or dislocations of the elbow joint, in addition to osteomyelitis and arthritic changes. It is the preferred projection to assess the medial and lateral epicondyles of the humerus for avulsion-type fractures 2,3.

Radiographic Anatomy Paediatric Elbow AP Elbow anatomy, Medical
This is often the only X-ray sign of a bone injury. A post-traumatic effusion without a visible bone fracture usually indicates a radial head fracture in an adult, and a supracondylar fracture of the distal humerus in a child. If there is a joint effusion but no history of trauma, an inflammatory cause should be considered.

Pin on Xrays
Access my FREE Online Membership today → https://www.thenotedanatomist.com___Unlock my Premium Tutoring Memberships → https://www.thenotedanatomist.com/premi.

xray AP Elbow Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
I've created a radiology physics question bank. Check it out here 👉 https://www.radiologytuts.com/courses/xray-physics-question-bank Let's revise how to rea.